Papaya cultivation in India is a very profitable and relatively safe agriculture business. Papaya can be cultivated for vegetable, fruit, latex and dry leaves. Discover how to start papaya farming in India and make profit.
Papaya, also known as pawpaw is a delicious fruit rich in vitamin C. It is a tropical fruit and is highly valuable medicinal ingredient. Originally from Costa Rica and South Mexico, it is now widely cultivated worldwide. Globally, India leads the world in papaya production followed by Brazil, Mexico, Nigeria, Indonesia, Peru, China, Thailand and Philippines. Being a highly productive crop and easy to grow papaya is cultivated widely as a kitchen garden in India.
Papaya Tree Information

Papaya belongs to the family Caricaceae. Botanically called as Carica papaya, it occurs in three sexes- male, females and hermaphrodites. Papaya plant grows straight up to 16 to 33 feet tall. They branch only when there is a damage at the apex of the stem; otherwise they are unbranched. The leaves are shaped like a fan and have a long stalk. The flowers are dimorphic and have 5 petals. The stamens of the male flowers are fused along with the petals whereas the female flowers have contorted petals with a superior ovary. The petals are attached loosely at the base of the flowers. They usually open at night and are pollinated by moths. The fruit varies in shape from oblong to spherical and it is orange colored when ripe.
Ideal Conditions for Papaya Cultivation in India
Being a tropical plant a tropical weather is most suited for papaya plantation. It can grow in almost all types of soils.
Climate for Papaya Cultivation
Being a tropical crop, papaya crops need a high level of humidity and temperature. It is sensitive to frost and heavy rains can cause damage. It can also grow in subtropical areas. Areas near the foothills have been found to be the perfect place for papaya cultivation in India. It can grow well at sea level and up to 600m of altitude from sea level. Above 600m, the fruits decrease in quality. Although the crop favors high levels of humidity for growth, it needs a warm and dry climate for ripening. The roots being shallow, papaya plant cannot withstand strong winds. Papaya can also be cultivated in greenhouse farming.

Soil for Papaya Plantation
Papaya can grow in a variety of soils. However, a rich, sandy loam is ideal for papaya plantation. It can also grow well in alluvial soil which is found along the deltas and river banks. However, it cannot grow in shallow soils or soils that do not let water drain off easily. A fertile, lime-free and well-drained soil is preferred for papaya cultivation.
pH Requirement in Papaya Farming
A neutral to near neutral soil can be used for papaya cultivation. The pH can be between 5.5 and 7.5.
Season for Papaya Plantation
Papaya is planted during monsoon, autumn and spring season. It is not planted during winter as the frost can cause damage or injury to the crop. In other words, they are planted during the months of June-July (monsoon), October-November (autumn) or February-March (summer). The first few things to be considered while planting papaya are rain, frost and hot air since all three cause injury to the plant.
Watering Papaya Plant
Water requirement for papaya depends on the environmental factors of the area like light, temperature, rainfall, wind, soil type, etc. It also differs with the age of the plant. A young papaya plant would need more moisture than the older trees. This is because older trees have slower vegetative growth. Hence the seedlings are irrigated once or twice a week while fruit bearing trees need irrigation once in every 15 days. Older trees need ample water. However, they cannot tolerate stagnated water or water logging since their roots are shallow and not deep. It results in ‘wet feet’ and lower fruit yield. That’s why drip irrigation in papaya plantation is a good practice. During winter, papaya must be irrigated at an interval of 10-12 days while in summer they are watered once a week till the rains begin.
Crop Rotation with Papaya
Papaya is generally rotated with crops like sugarcane, bamboo, cereals, reeds, etc.
Planting Material for Papaya Farming

Papayas are commercially propagated through seeds. Although tissue culture technique of growing papaya has been developed, they are restricted to laboratories. Papaya seeds cannot be stored for long unlike other seeds since they lose their viability quickly. They are first planted in nurseries in poly-bags. The newly-germinated young seedlings are then transplanted after 6-8 weeks.
Papaya Varieties
Different varieties have been developed for papaya cultivation in India. These varieties can be divided into 2 broad categories:
- Dioecious- producing separate male and female plants
- Gynodioecious- producing female and hermaphrodite plants
Some of the important commercial varieties commonly cultivated by farmers in India are:
Pusa Delicious
- Mainly cultivated in Jharkhand, Orissa, Karnataka and Kerala.
- Medium-sized plants
- First fruiting within 253 days of planting at a height of 80 cm.
- Gynodioecious, high-yielding variety.
- Individual fruit weighs 1-2 Kg
- Distinct flavor and moderate keeping quality.
- Flesh is deep orange in color
- Total plant yield is about 41 Kg per plant.
Pusa Dwarf
- Dwarf-sized plants
- Starts fruiting at 40 cm height
- Dioecious plant variety
- Fruits vary in shape from oval to round.
- This variety is suitable for kitchen gardening and also high density cultivation.
- Individual fruit weighs 0.5 to 1 Kg.
- Per plant yield is about 40 Kg.
Pusa Giant
- They bear their first fruit when they are a meter tall.
- Fruits are yellow with moderate firmness.
- They are dioecious.
- Individual fruit weighs 2-3 Kg.
- Yield per plant is 40 Kg.
Pusa Majesty
- Fruit bearing starts when the plant attains a height of 48 cm within 245 days.
- Gynodioecious plant.
- Fruit is orange-colored with a firm pulp.
- It is suitable for long distance transport since it has a long shelf life.
- Individual fruit weight is 1-1.5 Kg.
- Total per plant yield is 38 Kg.
Pusa Nanha
- Popular in Jharkhand, Orissa, Karnataka and Kerala.
- It is a mutant variety of dioecious dwarf.
- Plant bears fruits at 30 cm height and total height attained by the plant is 106 cm.
- Suitable for pot cultivation, high density papaya plantation.
- Tolerant towards water logging conditions.
- Medium sized fruit with round to oval shape.
- Per plant yield is 10.1 Kg.
Sunrise Solo
- Popular in Andhra Pradesh
- It is an improved variety of Hawaiian variety called Solo.
- Fruit is pear shaped, smooth; red colored and has a mild flavor.
- Individual fruit weigh is about 400-500 grams.
- Per plant yield is 20 Kg.
Arka Surya
- Variety developed by crossing Sunrise Solo with Pink Pulp Sweet.
- The fruits are medium-sized and firm with pink colored pulp.
- Individual fruit weighs 600-800 grams.
- Individual plant yield is 60-70 Kg
- The cropping period for this variety is 28 months.
Arka Prabhath
- Advanced hybrid resulting from the cross between Surya, Tainung-1 and Local Dwarf.
- The fruits are large in size with firm and deep pink colored pulp.
- Individual fruit weighs 900-1200 grams.
- Yield per plant is 90-100 Kg.
CO-1
- Popular in Andhra Pradesh
- It is a dioecious variety that was developed in Tamil Nadu Agricultural University, Coimbatore after working for eight years.
- Fruits start developing when the plants attain a height of 60-75 cm.
- Size of the fruits range from medium to big with a flat base, ridges at the apex and a slight nipple.
- The fruit pulp is orangish to yellow in color with medium firmness.
- It does not contain the papain odor.
- Individual fruit weighs around 1.5 Kg.
- Per plant yield is 50-60 fruits in a period of 20 months.
CO-2
- Popular in Andhra Pradesh
- Dioecious variety of papaya developed from a local type by Tamil Nadu Agricultural University, Coimbatore.
- The fruits are large sized with orange colored pulp.
- Pulp firmness is soft and they are moderately juicy.
- Individual fruit weigh 1.5-2.5 Kg.
- Per plant yield is 80-100 fruits.
- It is also cultivated for its latex papain and it yields about 30 grams of latex.
CO-3
- Popular in Andhra Pradesh
- Developed by crossing CO2 and Sunrise Solo by Tamil Nadu Agricultural University, Coimbatore (TNAU).
- Gynodioecious hybrid.
- Pyriform, smooth fruits with firm, red pulp.
- Individual fruit weight varies between 450 to 800 grams.
- Per plant yield is 90-120 fruits.
CO-4
- Dioecious variety developed by crossing CO1 with Washington by TNAU.
- The plant has a purple coloration.
- Fruits are medium-sized, round-shaped with firm, yellow pulp.
- Individual fruit weighs 1.3 to 1.5 Kg
- Total per plant yield is 80 fruits over a two-year period.
CO-5
- It is a dioecious variety of Washington developed by TNAU.
- The papain content is very high in this variety.
- Suitable for table purpose.
- The fruit is yellow with soft pulp moderate in firmness.
- Each individual fruit weighs 1.5 Kg.
- Total yield per plant is 80 Kg of fruits.
- This variety also yields about 600 Kg of dried papain per acre.
CO-6
- A dwarf selection from Giant papaya by TNAU.
- It is a dioecious variety.
- The fruit size is large and the pulp is yellow with moderate firmness.
- Individual fruit weighs 2 Kg.
- Yield per plant is 80-100 fruits.
CO-7
- It is developed by crossing Pusa Delicious, Coorg Honey Dew, CO3 and CP85 multiple times over a period of 4 years by TNAU.
- It is gynodioecious.
- Fruits are oblong in shape with red colored pulp.
- Individual fruit weighs about 1.15 Kg.
- Total yield per plant is 98 fruits per tree for a cropping period of 28 months.
CO-8
- It is a red pulp variety of papaya developed by selective hybridization and intermating.
- They are popular for making desserts, jams, other processing food and papin.
- Fruits produced are large in size and oblong.
- Individual fruit weighs 1.5-2.0 Kg.
Taiwan Red Lady Papaya Cultivation
This is a new variety of papaya and very popular among farmers in recent years. Red lady papaya is very large in size and is cultivated for fruit purpose.
Land Preparation for Papaya Plantation
The land meant for papaya cultivation must be well-protected from strong winds and must not get waterlogged easily during rains. In case of strong winds, there must be windbreaks around the land. The seeds are first sown in nurseries and the seedlings are transplanted to the main field after about 6-8 weeks of growth.
Before transplantation, pits of dimensions 50cm X 50cm X 50cm are dug a month and filled with farm yard manure, organic waste and soil. 2-3 seedlings are transplanted per pit. When the plants start flowering only one plant per pit should be kept. In order to avoid weeds, hoeing is done regularly for the first year. Once the plants start flowering, only 10% male plants are kept scattered in the orchard while the rest are removed.
Intercropping in Papaya Cultivation in India
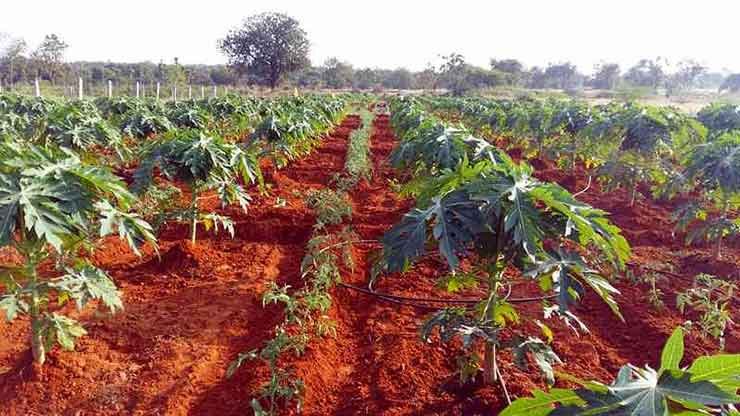

Papaya is intercropped with crops like coconut, peanut, pineapple, jackfruit, coffee, etc. in India. They are also planted as fillers for litchi, guava and mango. This is mainly because they stay on field for 2-3 years. In case papaya is cultivated in the entire orchard, then vegetables like garlic, turnip, onion, cauliflower etc. are grown for the first year. However, no crops are cultivated alongside after the first year since competition for nutrition is likely at later stages.
Frost Protection in Papaya Farming in India
Since papaya is sensitive to frost, in North India, papaya cultivation must have adequate frost protection. Frost occurs during the months from December to February. Generally, planting is done before the onset of winter. In addition, the plants are covered by thatching around them with polythene bags of the plant size. The bags must have air holes punched in them on the upper side. This is for the first winter. The next year, gunny bags can be used to wrap the plant around the fruit and at the apex.
Diseases in Papaya Plantation
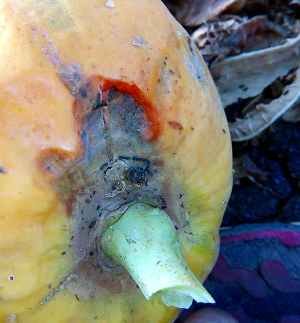
The main diseases that affect papaya crop are anthracnose, powdery mildew, stem rot and damping off. Water logging around the roots is the chief reason for rots to occur. Wettable Sulphur, carbendazim and mancozeb are effective in controlling these diseases.
Aphids, red spider mite, stem borer, fruit flies, grey weevils and grasshoppers are the insects attacking papaya plants. Destroying the infected part and spraying prophylactic spray like 0.3% dimethoate would help control them.
Harvesting Papaya

When the fruits are fully grown and start developing a tinge of yellow color at the apex, it is time to harvest them. Another indication of harvesting time is the latex. Once the latex start turning watery instead of being milky, the fruits must be harvested. Not all papaya varieties turn yellow on ripening. Some turn yellow while others remain green even when fully ripe.
The economic life of papaya lasts for a maximum of 4 years. However, farmers do not extend its life beyond 2-3 years as from the 3rd yes production decreases. Good farm management and timely care can increase papaya production to a great degree.
Post-Harvesting Practices
At the time of harvest, papayas must not suffer any injuries or blemishes. These can cause a risk of fungal contamination. In that case the fruits would start decaying quickly thus reducing their market value. Since they are perishable fruits, each individual papaya must be wrapped separately in paper and then placed in wooden crates. The crates must be filled with straw, sawdust and other such soft material to protect the papayas from transportation injuries.
Conclusion
Papaya cultivation does not require too much hard work. It is a versatile crop and can be cultivated for vegetables, fruits and latex, even the dry leaves has market value as raw material for medicine.
Reference

Please guide me, I need your help
You may buy our project reports for detailed economical and technical information.
I got lot of information about papaya. If included how many plants per acre ?, Organic cultivation method, fertilizer requirements very beneficial.
Thank you.
I am going to plant Red lady papaya for the first time and I have no previous experience .So if I could get some help I would be much thankful for helping me.
I am planning to cultivate this papaya in ooty.
Is this climatic condition will support to this plant. Pls let me know.
Papaya does not support extreme cold weather.
सर मैने पहली बार रेड लेडी ताईवान पपीते का रोपण किया है,,मेरी जमीन रेतीली है,,मैने रोपण के दोरान 1,50कि• कम्पोस्ट खाद +कार्टाफ10 ग्रा•/पोधा+25ग्राम पोटाश दिया है,,रोपण के तुरंत बाद सिचाई की है,,5से6दिन सिचाई हो गये कुछ पोधे मुर्झा रहे है,,खेत सूख चुका है,,सर पानी देना चाहिऐ! कृपया मार्गदर्न किजिऐ ! देवेन्द्र कुमार (रूडकी) हरिद्वार (उत्राखण्ड)
Hi,
Where can I find the papaya seeds for farming?
Try nearest nursery and ask for branded seeds in closed packet.
I m interesting in doing papaya farming near about one bigha area.. plants have been arranged from Pune , Maharashtra. I may need your suggestion in time to come ahead.
Koi Bihar ya up me papita Ka kheti kiya hai to please btaiye
15 acres in kankavali sindhudutg
Need some one who will take on contract farming of papays
I want start contract farming
Want to start papaya cultivation in 1 acre,needs support
महोदय!
मैं भजनलाल गुप्त हरदोई (उत्तर प्रदेश) -241001
पपीता की खेती करना चाहता हूँ,हमारी भूमि बलुई दूमट (सेंडी स्वायल) है !
कौन सा बीज उपयुक्त रहेगा,कहाँ से प्राप्त होगा?,पौधों की सघनता (लाइनवपौधे की दूरी, बीज वुबाई नर्सरी, प्लांटेशन का समय, परिपक्वता अवधि, पौधे कितने बर्ष तक फल देगा? उत्पादन एवं अन्य कृषि व्यवहार !
कृपया बताने की कृपा करें !
i want to grow papaya in punjab in between rows of kinnow .pl advise best time and suitable variety.
Info for our land in the 1hactor in2500 plents in male will be in 40/ what I can do for that plants idonow how to do please let us do for you think about male plents
I want to start papaya farming in panjab plz suggest me good variety of papaya or any contract farming
papaya Kashmir mea cultivation kar sakta hai
i want to grow papaya in Kashmir (jammu & Kashmir